February 4, 2019
PSD2 regulation will change the European financial services market forever. Open Banking helps the financial sector to make a huge jump to catch up with the rest of the industries in terms of digitalization of the services and customer experience. Moreover, PSD2 implementation will give all fintech companies new huge opportunities to increase their service speed, security, accessibility, coverage, and grow client base. After all, those are the key factors that help business to win competition in 2019. In this article, we will explain, how financial services provider can benefit from new PSD2 regulations.
European retail banking is bound to face new challenges as well as new opportunities. PSD2 and recent EBA (European Banking Authority) regulations open a wide range of possibilities for the fintech companies. So what is PSD2 regulation?
List of the contents:
- What is PSD2 regulation and what are its main goals
- PSD2 as the new opportunities for the fintech companies
- Change example: What will happen to screen scraping bank accounts
- In conclusion
WHAT IS PSD2 REGULATION
PSD2 (Revised Payment Service Directive) is the directive issued by the European Commission for innovation improvement and internet payment safety. It deals with improving cross-border payments, account access security, and reinforcement of customer protection around EEA. The first European payment services directive was voted in by the Parliament and came into force in 2007. PSD established a new legal payment framework of the EU. Furthermore, the revised directive is not just an updated version of PSD, this is an extension of the previous one.
Main objectives of PSD2
PSD2 regulation is all about creating open banking in EEA, whereas providing online payment safety by certainly defined rules. This directive authorizes bank customers to use the services of third-party providers. New PSD2 regulations enable both customers and businesses to manage finances in a more convenient way with the wider choice of providers. In addition to that dense legislation, PSD2 covers online safety of the customer. In short, customers will be able to use the services of different providers, for example analyzing their spending, paying bills, or making some transfers, as long as their money is deposited safely within their bank accounts. All the banks are obliged to create the system of open APIs that gives access to the accounts. With this access, third-party providers have become authorized to provide various financial services using bank data in order to facilitate customers’ experience. It goes without saying that banks will get new competitors that offer financial services not only among banks themselves but every provider of financial assistance.
The current situation in the financial services market
Except for the customers themselves, the banks and financial institutions with banking licenses are the sole owners of access to consumers’ financial data and completely in charge of all the accounts. The first question that might arise is “Why would I give anybody access to my bank account except the bank?”. The reality is much more complex. For example, working with loan firms and insurance companies is way more complicated for the ordinary consumer that it might be. Simply because those third- party providers cannot get access to the data they need even if they have the client’s consent. The client should go to the bank, get the paperwork done, repeat. In cases, when such third-party providers indeed have access, they’re almost all the times have an exclusive partnership with the bank which restricts the list of the offerings available for the client. Moreover, this access is also limited to one country even if you’re living in the EU. For a quite long time, we used to feel free to buy retail goods and services from all around the globe, which provides huge flexibility and variety of choices. Unfortunately, this is not the case with financial service. Not to mention the enterprise companies who have dozens of accounts in various banks across all the world. The most simple example here is that the accounting software usually doesn’t have the needed capabilities and integrations to even display all the accounts status in one place, because this would require software companies to have the agreement with a lot of banks and customer integration with very diverse banking IT systems. This pushes enterprises and accounting software vendors to use workarounds such as screen scraping of bank accounts, which is a very huge compromise between convenience and security.
Before PSD introduction in 2018 banks and financial institution were the sole owners of the financial data
Right now, third parties financial service providers face great challenges when it comes to using banking data and interacting with the functions provided by the banks’ IT systems. For instance, if you want to build a simple mobile app that analyzes user’s spendings and make some suggestions for savings, you got to get a bank’s consent to access their internal IT service, efforts from the bank IT department to make it accessible to your engineers and make a custom integration with that banking system which will be useless for work with other banks. Not to mention all the compliance issues and legal work. This complex workflow should be repeated with each bank in each country. Covering only one country will be an extremely tough, long, and expensive process for such a startup.
PSD2 regulation is aimed at unification of the financial market across the EU and make all the services available to everybody regardless of the particular residence within EEA. Basically, PSD2 is changing the current banks’ position as the major providers of financial services. The position of third-party providers was limited in some ways as it had required bank licenses and made it problematic to access the market and offer any financial services. Also, it was caused by a lack of trust in them. Fortunately, PSD2 regulation is about to change this, because fintech companies have a lot of great solutions. They are ready to enter the investment market and become decent competitors. PSD2 implementation will greatly change the payment models, open new possibilities for financial providers while both customers and businesses will considerably benefit from implementing PSD2.
History of PSD2 and timeline of the regulatory measures
EBA decided to vote for the final version of PSD2 in December 2015 in order to implement innovations, improve security and employ cross-border banking. In a month PSD2 regulations came into force and members of the EU started implementation into national laws with a 2-year deadline by January 2018. RSD2 has opened more possibilities, however, it requires some time and good regulations of implementing.
European Banking Authority headquarters
The final version of the regulatory technical standards (RTS) on secure user authentication and standard and secure communication (SCA and CSC) was published in June 2018 to clarify additional measures. The EBA aims to provide guidance for market members and help with the implementation of RTS on SCA and CSC, that will come into force from September 14th, 2019.
PSD2 REGULATIONS AS NEW OPPORTUNITIES FOR FINTECH COMPANIES AND STARTUPS
The European Commission aims to open the EEA market for different providers. On the one hand, PSD2 implementation is quite a long process that requires time and a lot of effort. The generally accepted position of banks as the major providers at the financial markets greatly influences public opinion. Regular users would rather choose licensed banks instead of third-party providers. On the other hand, the fintech companies and third-party services have already recommended themselves as highly qualified, secure organizations. Thus there are no practical reasons to restrict consumers’ choice besides the banks’ aspiration to keep their market positions. In this situation, PSD2 regulation keeps on unifying the European market, encouraging the third-party providers’ services when they attain the license of the state financial authorities. The unified market attracts different entrants and stimulates the development of new financial approaches.
What new PSD2 regulation gives to the fintech companies?
Shortly, PSD2 gives anybody legal and technical tools to build their applications and services on top of banks’ data and services. For example, a startup from Italy can get access to the financial data in France as simple as to the same data in Italy. Since the competition increases, customers are informed much better and have a more diverse choice and are more likely to purchase online from international companies. All those changes caused by implementing PSD2 encourage investment in the European financial market. That gives the chance for all the providers with legal frameworks to operate not only in their home country but in other countries of the EU.
PSD2 regulation was among the main subjects on xCeed Fintech Conference 2018
The point is that this market is open to both European and international banks as well as non-banks providing financial services. Those innovations are inevitable due to the development of technologies as well. Modern technologies have changed the preferences of the customers and the business frameworks in general. That made the banks be aware of and apply the technology for the banking framework and even renovate business models. More and more banks are collaborating with fintech companies to meet up-to-date customers’ requirements. People need easier and faster payment systems, thus contactless payments and mobile services strengthen their position in the market. Some banks might be hesitant with applying technologies because they are not in entire control anymore. Moreover, the percentage of customers who use financial service only by applying new technologies sharply increases.
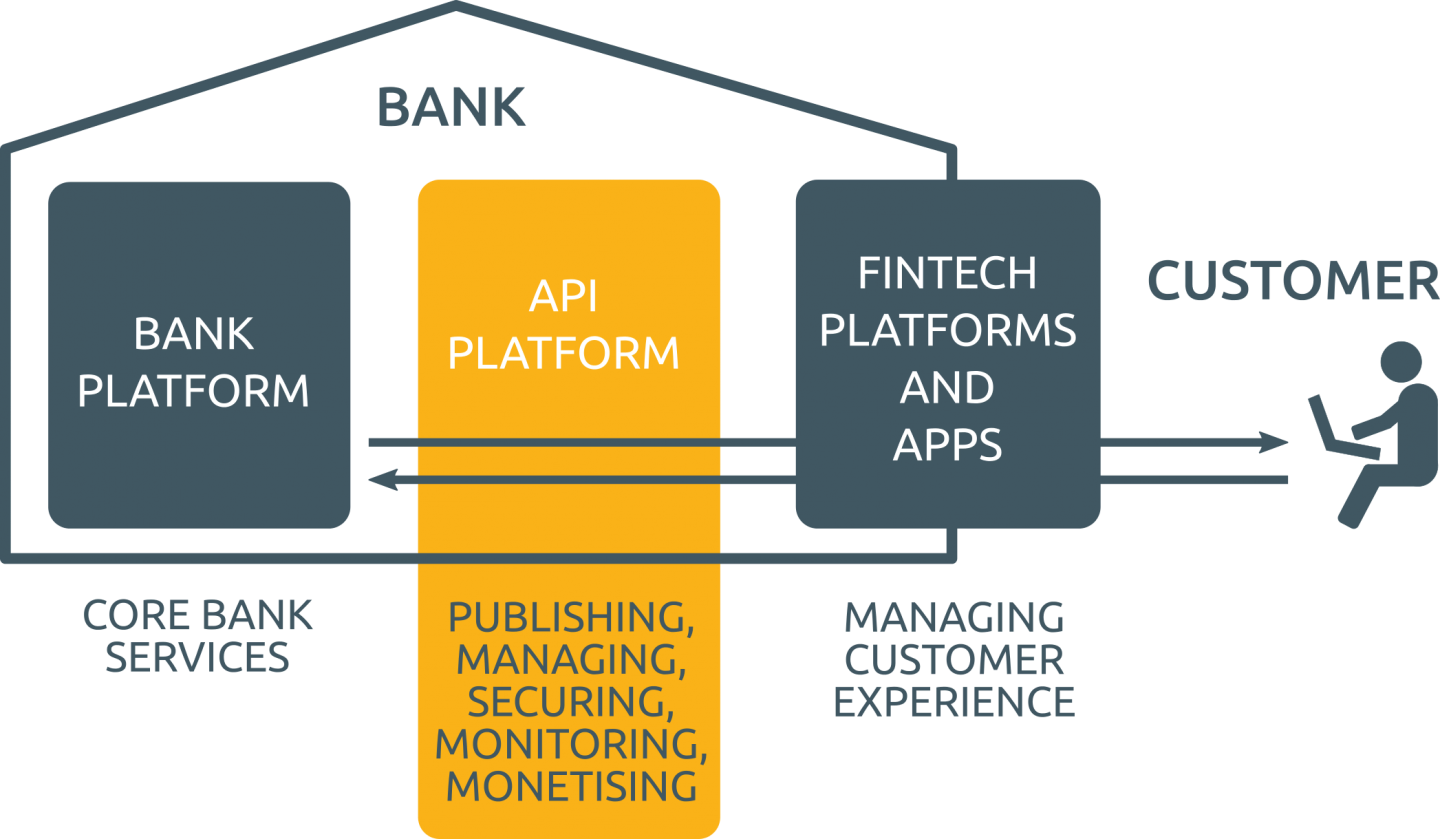
Open Banking project and APIs
Open Banking is a synonym to PSD2 and comprises the set of measures that banks are obligated to apply in order to help third-party providers to build their fintech applications and services around the banks, their information, and internet banking systems functionality. It all goes down to APIs and how banks should provide access to those programming interfaces.
Therefore banks started innovation improvement using different resources and the help of the fintech companies to manage their customer services. PSD2 regulations expend service offers for the customer and businesses through the general system of APIs. Putting to use open APIs financial providers are able to enter the market, bring new ideas for the better banking experience. Of course, their infrastructure is rather different from the banks’ one and compliance isn’t that heavy. Just because those providers are not offering the complete package, their task is to concentrate on providing a certain service using the data and services at banks’ disposal through open APIs. Customers call for personalized, informal, fast access and cheaper fees. The fintech companies have applied this approach successfully concentrating on customer-oriented and digital ways rather than traditional ones.
The new structure of the financial services after Open Banking implementation
Banks only started to introduce their open APIs and there is a long way until everything will be settled up and standardized. While PSD2 enforces banks to give third parties access to their data, API is a very broad term and there are still some misunderstandings and misconceptions on how those Open Baking APIs should look, work, what technical documentation to be provided, etc. Yet, fintech companies at once gained access to the data and new features they couldn’t imagine a couple of years ago. This leads us to the conclusion, that 2019 is the high time to use all those new opportunities and jump into the competition while the market is still not overcrowded.
Open API obligations for banks
For now, the main task of the European payment services directive is regulating all appointed obligations for the banks and the third-party providers in a proper way. Right now, there is an issue with letting someone access to your bank account in order to help you to provide a loan or medical insurance company. In order to do that, the user should share his internet banking credentials or go to the bank and extract the information manually which requires time and effort. Those credentials automatically give third-party full access to all functionality of internet banking. One of the main tasks of the Open Banking regulations is to make everyone’s life a bit easier and avoid the situations when service providers get the access they actually don’t need to make their application work. In order to do that two new participants of the financial framework will be introduced – PISP and AISP. Those are mainly the two different levels of access and each fintech company can apply and comply with only one type of accreditation. Let’s define them:
- Account Information Service Provider (AISP) is the service provider that has access to the information of the customer bank account. They are set to analyze customer’s banking activities, accumulate the information from different accounts into one review.
- Payment Initiation Service Provider (PISP) is the service provider that is authorized to launch the payment on behalf of the customer like bill payment, transfer, and other financial services.
In addition, banks face economic challenges. IT expenses are likely to increase, banks should provide an open and secure system of APIs for collaborating with the third-party providers. PSD2 is a good solution for providing security for both customers and businesses because a secure authentication process is strongly required from the major providers as well as third-party providers. For the first time, the common regulations on banking are going to be implemented. The revised directive is giving a clear description of the overall service, duties, and regulations. Implementing PSD2 still requires time and happens to be more transparent, provides clarification of technical changes, and what providers are responsible for.
Separate and exclusive agreements are not necessary anymore
Close collaboration is great. That is for sure. But not that great if you’re fintech startup and must make separate agreements with five different banks to cover 65% of users in just one country. PSD2 regulation makes that so much easier.
Now, fintech company can apply to be certificated as beforementioned Account Information Service Provider or Payment Initiation Service Provider to become an approved third-party with access to the APIs. And that makes banking data and operations available for the companies related to finances. Immediately. Sure, there will be some work required to integrate with that open banking APIs. But it will be incomparably smaller to the amount of work needed to custom integrate with dozens of banks. For example, according to openbanking.org.uk 99 organizations have been already certified as such providers at the moment of this article publication (February 2019). In April 2018 there were only 18 of them listed. As we can observe, the process of approval goes pretty well.
While competition increases, it always brings certain advantages through the implementation of PSD2. European payment services directive dismisses barriers to enter the market for the financial service providers without the banking license. In short, it is like a unique agreement with the banks for non-banks that can enter the market by applying APIs systems.
Those can be the same providers as for your mobile application but have certain access to the information of your bank account, and help with initiating assistance in chosen tasks. Consequently, customers will be using only the best service of their own choice.
DISRUPTION EXAMPLE: IS SCREEN SCRAPING OF BANK ACCOUNTS NOW OFFICIALLY DEAD?
The techniques of screen scraping bank accounts are widely used to access the customer’s data. It is the software-driven and automated usage of a website to extract certain variables. In simple words, screen scraping or data scraping application just emulates the user and makes internet banking “think” that it is the human who works with the computer via a standard web browser and graphical interface. The fintech companies prefer to apply screen scraping banking due to the lack of open APIs and use the customers’ interfaces that are available for them. According to PSD2, screen scraping open banking is being considered as “direct access”. Consequently, the third-party companies can have a record of the customers’ login credentials for logging into the banks’ accounts automatically and extract the needed information. For example, customers’ expenses for certain goods or services. But at the same time, they have access to other users’ data and theoretically can perform some actions on behalf of the user. The most simple example is the ability to transfer money between accounts for the application that need only the data about the account balance. Potentially, this can lead to fraud.
PSD2 regulation requires more liability to initiate the payment by the service provider, compared with the current situation. The European Commission considers open banking screen scraping as attaining the customer data through their interfaces by using their security credentials without any identification by the bank side. As it has been said above, screen scraping applications “fool” internet banking systems into considering them as humans. Due to the revised directive, the European Commission improves the security of online payments and access to the bank accounts while protecting the customer data from any unidentified providers. On the other hand, the banks might still choose interfaces: APIs or an identification layer in front of electronic banking. Thus the third-party providers are required to use APIs only as long as they exist and work properly. In other cases, they will receive access through electronic banking that is still dominated by screen scraping.
Actually, there are still a lot of discussions between the European fintech companies and the European Banking Authority around the released RSD2. Definitely, it opens new opportunities for third-party companies however PSD2 regulation changes their frameworks completely. EBA makes the providers abolish screen scraping of bank accounts. And for many fintech companies, it requires some certain clarifications because open banking screen scraping is what they are currently using for most of their services.
Problems with screen scraping
It is admitted that screen scraping banking has a number of problems that APIs completely lacs. Screen scraping bank accounts compel the provider to store the customers’ credentials which are needed to be accessible and, often, unencrypted. It is rather dangerous for the leak of the data. There weren’t any reported incidents so far, however, everyone understands that even more can be done and improved for security reasons. What is even worst, open banking screen scraping legislates and makes the customers get acquainted with passing their credentials to third-party companies.
Besides that, screen scraping banking always depends on any changes in bank interfaces. It can be whether the whole interface redesign or just the location of some elements. Each time it requires the manual fix for solving this problem anyway. One changed button can interrupt the services provided by the whole accounting software company. Therefore, the provider should spend time, resources for handling the issues.
Screen scraping or Open Banking?
Open Banking API is by far better alternative to screen scraping which initially was just a workaround to avoid direct collaboration with banks via long and painful integration with their services.
Analyzing all pros and cons, we can say that PSD2 is a great alternative offering new options for banking frameworks unifying innovations and the security of the customers. PSD2 regulates that the customers’ data will be given to the trusted third-party companies approved by EBA and help to solve a lot of issues with screen scraping. It provides the customer with security by establishing the open system of AIPs. The banking frameworks are going to become more stable due to the consistency of platforms. Definitely, RSD2 is the future of banking that will take some time and clear regulations for implementing all standards. It is argued that PSD2 will make screen scraping banking dead. It will be used in a foreseen future unless all the services will be standardized. There are even companies like Mozenda building their business around providing customers with the tools for the screen scraping including the banking data. The European Commission’s decision on voting in for PSD2 helps to provide the security and implementing innovations for the benefits of the customers, third-party providers, and banks.
IN CONCLUSION
Taking into account all the mentioned details, we can reach the conclusion that PSD2 regulation facilitates managing the financial services and opens the regulated market entry for fintech companies. This causes a lot of advantages like increased security, an open system of APIs, and fair competition. It might be a sophisticated way of connecting innovations and compliance, but definitely, it is worth it. It is like changing the rules of the game for the gain of both sides.
We hope this article helped you to find out more details about PSD2 regulations. Existek is an offshore software development company that helps you and your business to deal with various innovations. If you need professional help in the development of an excellent financial application, feel free to contact us at our contact page or start the dialogue in the chat widget to the right and we will be glad to assist you.